Advantages of smart grids lie in their ability to revolutionize the energy sector, offering a glimpse into a future powered by efficiency and sustainability. As we delve into the realm of smart grids, we uncover a world where environmental benefits, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced security converge to shape a brighter tomorrow.
Smart grids not only pave the way for a greener planet but also promise a more reliable and cost-effective energy distribution system. Let’s unravel the myriad advantages that smart grids bring to the table in our quest for a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Overview of Smart Grids
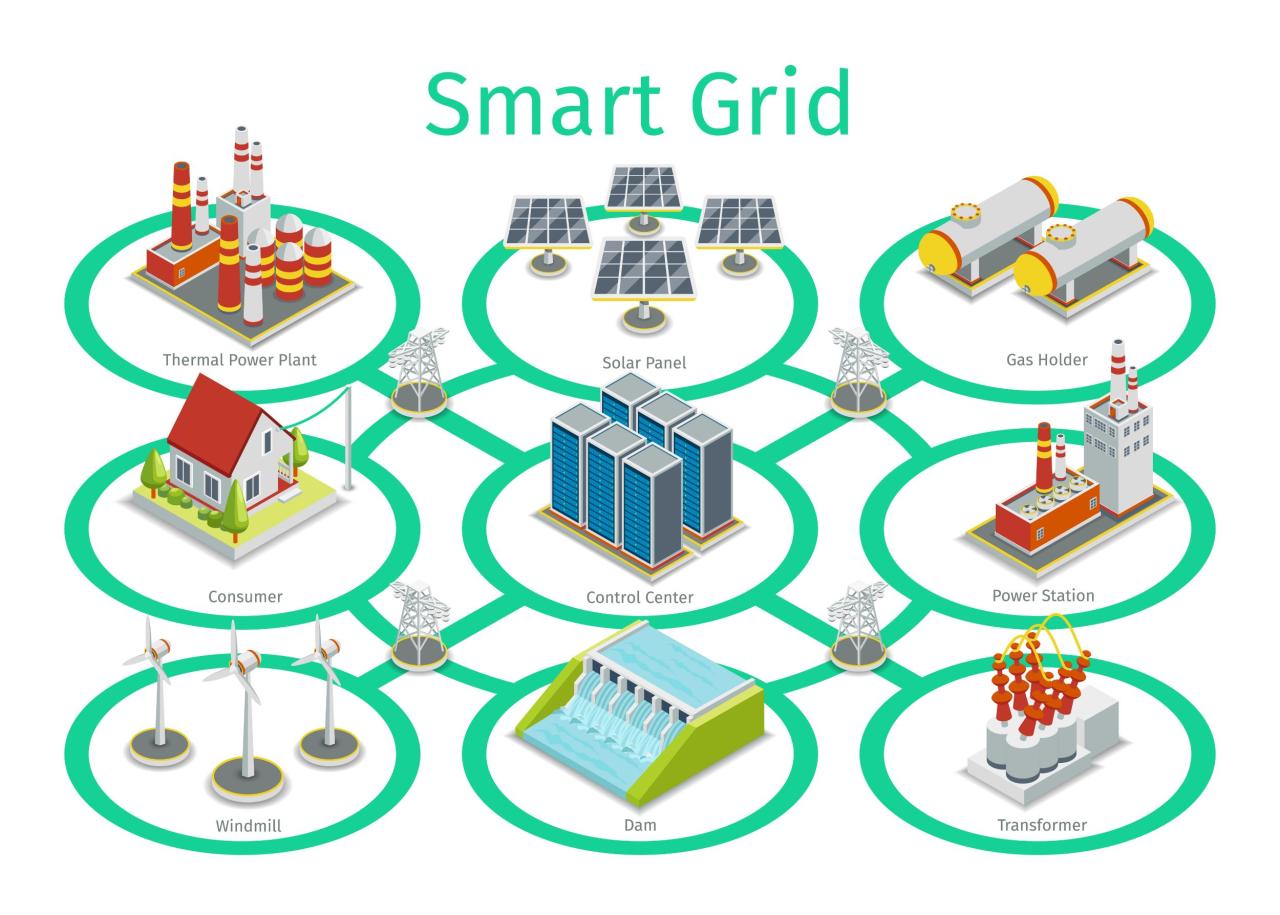
Smart grids are modern electricity networks that utilize digital technology to monitor and manage the flow of electricity more efficiently compared to traditional power grids. Unlike traditional grids, smart grids are equipped with advanced communication and control systems that enable real-time data collection and analysis.
The primary purpose of implementing smart grids in the energy sector is to improve reliability, resiliency, and sustainability of the power supply. By integrating renewable energy sources, energy storage systems, and smart meters, smart grids can optimize energy distribution, reduce outages, and enable better demand response.
Technologies Used in Smart Grid Systems
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): Smart meters provide real-time data on energy consumption and allow for two-way communication between utilities and consumers.
- Distribution Automation: Automated systems help to detect and isolate faults in the grid, minimizing downtime and improving overall reliability.
- Microgrids: Localized grids that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, enhancing energy security and efficiency.
- Energy Management Systems (EMS): Software applications that optimize energy generation, distribution, and consumption based on real-time data and forecasts.
Advantages of Smart Grids
Smart grids offer numerous advantages that go beyond just efficient power distribution. Let’s explore some of the key benefits below:
Environmental Benefits of Smart Grids
Smart grids play a crucial role in promoting environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and fostering the integration of renewable energy sources. By enabling the efficient management of energy resources, smart grids help minimize the environmental impact of traditional power grids. These systems facilitate the seamless integration of solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources, thereby reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a cleaner and greener energy landscape.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
One of the primary advantages of smart grids is their ability to enhance energy efficiency and promote conservation. Through advanced monitoring and control capabilities, smart grids optimize energy consumption, reduce wastage, and promote a more sustainable use of resources. By providing real-time data on energy consumption patterns, smart grids empower consumers to make informed decisions about their energy usage, ultimately leading to reduced energy bills and a more sustainable energy future.
Reliability of Smart Grids
Compared to traditional grids, smart grids offer significantly higher reliability in power distribution. The advanced monitoring and communication capabilities of smart grids enable real-time detection of faults, quick response to outages, and efficient rerouting of power to minimize disruptions. This enhanced reliability ensures a more stable and resilient power supply, reducing the likelihood of blackouts and improving overall grid performance.
Cost-Effectiveness of Smart Grids
Smart grids offer significant financial advantages by optimizing energy distribution, enhancing system reliability, and reducing operational costs. This results in cost savings for both utility companies and consumers.
Operational Cost Reduction
Smart grids enable utilities to remotely monitor and control electricity flow, detect and respond to outages more efficiently, and integrate renewable energy sources seamlessly. By automating processes and improving system efficiency, smart grids help reduce maintenance costs and operational expenses significantly.
Peak Load Management
One of the key advantages of smart grids is their ability to manage peak loads effectively. By implementing demand response programs and time-of-use pricing, utilities can incentivize consumers to shift their energy consumption to off-peak hours. This helps reduce strain on the grid during peak times, avoiding the need for expensive infrastructure upgrades and ultimately lowering electricity costs for all consumers.
Grid Optimization and Asset Management
Smart grids allow for better optimization of existing infrastructure and assets, prolonging their lifespan and reducing the need for costly replacements. By utilizing predictive maintenance and real-time data analytics, utilities can identify potential issues before they escalate, minimizing downtime and maximizing the efficiency of the grid.
Consumer Empowerment
Consumers benefit from smart grids through increased awareness of their energy consumption patterns and the ability to make informed decisions about their usage. Smart meters provide real-time feedback on energy consumption, allowing consumers to adjust their behavior to lower their electricity bills. Additionally, dynamic pricing models encourage energy conservation and efficiency, leading to overall cost savings for households.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: Advantages Of Smart Grids
Smart grids play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources into the existing energy infrastructure. By utilizing advanced technology and communication systems, smart grids enable a seamless incorporation of clean energy sources into the grid, leading to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly power system.
Managing Fluctuations in Renewable Energy Production
One of the key challenges of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind is their intermittent nature, leading to fluctuations in energy production. Smart grids address this issue by implementing real-time monitoring and control systems that can manage and balance the variability of renewable energy generation. Through sophisticated algorithms and predictive analytics, smart grids can adjust power flow, store excess energy, and optimize resource allocation to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply.
- Smart grids enable the integration of energy storage solutions such as batteries, pumped hydro, and flywheels to store excess renewable energy during peak production periods and release it during high demand periods.
- Advanced forecasting tools and predictive analytics help grid operators anticipate fluctuations in renewable energy generation and proactively optimize grid operations to maintain grid stability.
- Smart grids facilitate the use of demand response programs that incentivize consumers to adjust their energy consumption based on real-time pricing signals, helping to balance supply and demand on the grid.
Smoother Transition to a Clean Energy Future
The integration of renewable energy sources is a critical step towards achieving a clean energy future and reducing carbon emissions. Smart grids play a pivotal role in this transition by providing the necessary infrastructure and technology to support the growth of renewable energy generation.
- By enabling the seamless integration of renewable energy sources, smart grids help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and accelerate the transition to a low-carbon energy system.
- Smart grids support the development of microgrids and decentralized energy systems, allowing communities to generate and consume their own renewable energy locally.
- Through enhanced grid flexibility and resilience, smart grids enable a more efficient and reliable energy network that can accommodate a higher share of renewable energy sources without compromising grid stability.
Enhanced Grid Security
Smart grids are equipped with advanced cybersecurity features that help protect the system from physical and cyber threats, ensuring the reliability and security of the energy supply. These security measures are crucial in safeguarding the grid infrastructure and data from potential attacks.
Cybersecurity Features of Smart Grid Systems
Smart grids use encryption, authentication protocols, and intrusion detection systems to secure communication between devices and the central control system. These features help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches, ensuring that the grid operates smoothly and securely.
Protection Against Physical and Cyber Threats
Smart grids have the capability to detect anomalies in the system, such as sudden spikes in energy consumption or unusual behavior in connected devices, which can indicate a potential physical or cyber threat. By identifying these threats early on, smart grids can take proactive measures to mitigate risks and prevent disruptions to the energy supply.
Importance of Grid Security, Advantages of smart grids
Grid security is essential for maintaining a reliable energy supply and preventing widespread outages that can have severe economic and social consequences. By investing in robust cybersecurity measures, smart grids can ensure the continuous operation of the grid and minimize the impact of potential security breaches on consumers and businesses.
Top FAQs
How do smart grids contribute to energy efficiency?
Smart grids optimize energy distribution, reduce wastage, and promote efficient usage, ultimately leading to higher energy efficiency levels.
What are the financial advantages of implementing smart grid technology?
Implementing smart grids can result in reduced operational costs, improved asset management, and increased revenue streams through optimized energy distribution.
How do smart grids enhance grid security?
Smart grids incorporate advanced cybersecurity measures to protect against physical and cyber threats, ensuring a reliable energy supply even in the face of potential security risks.







