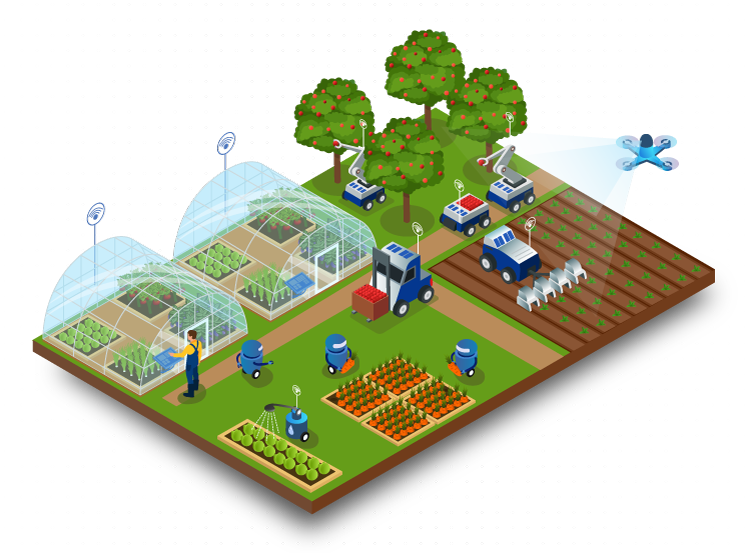
Embark on a journey into the realm of smart irrigation systems, revolutionizing the way we approach agriculture with cutting-edge technology and sustainable practices.
Exploring the intricacies of these systems unveils a world of efficiency, conservation, and modernization in farming techniques.
Overview of Smart Irrigation Systems
Smart irrigation systems utilize technology to efficiently manage water usage in agricultural settings, providing the right amount of water at the right time to optimize plant growth and minimize waste.
Traditional irrigation methods often rely on fixed schedules or manual labor to water crops, which can lead to overwatering or underwatering. In contrast, smart irrigation systems use sensors, weather data, and automation to tailor watering schedules based on real-time conditions and plant needs.
Benefits of Smart Irrigation Systems
- Water Conservation: Smart irrigation systems help reduce water waste by only watering when necessary, leading to significant water savings.
- Improved Crop Health: By delivering the right amount of water at the right time, smart irrigation systems promote healthier plant growth and increased crop yields.
- Cost Savings: With more efficient water usage and reduced energy consumption, farmers can save money on water bills and irrigation system maintenance.
- Convenience: Automation provided by smart irrigation systems eliminates the need for manual monitoring and adjustments, saving farmers time and labor.
Components of Smart Irrigation Systems

Smart irrigation systems consist of several key components that work together to efficiently manage water usage and maintain healthy landscapes. These components include sensors, controllers, weather data integration, and actuators.
Sensors
Sensors play a crucial role in smart irrigation systems by monitoring various environmental factors such as soil moisture levels, temperature, and light intensity. These sensors provide real-time data that helps the system determine when and how much water to apply to the landscape. By accurately measuring these parameters, sensors ensure that plants receive the right amount of water, reducing waste and promoting plant health.
Controllers
Controllers are the brains of the smart irrigation system, responsible for interpreting data from sensors and deciding when to activate irrigation. These controllers can be programmed to follow specific watering schedules based on the information gathered from sensors. Some controllers also have the capability to adjust watering patterns based on weather forecasts, further optimizing water usage.
Weather Data Integration
Integrating weather data into smart irrigation systems allows for a more dynamic and responsive watering schedule. By incorporating real-time weather forecasts, the system can adjust irrigation patterns based on factors such as rainfall, temperature, and humidity. This ensures that water is not wasted by watering unnecessarily during or after a rain event, ultimately saving water and reducing utility costs.
Actuators
Actuators are responsible for physically controlling the flow of water in the irrigation system. These devices open and close valves to allow water to flow to specific zones or areas of the landscape. Actuators work in conjunction with the controllers to ensure that water is distributed efficiently and effectively to meet the watering requirements of the plants.
Types of Smart Irrigation Technologies
Smart irrigation technologies have evolved over the years to offer efficient and sustainable solutions for water management in agriculture and landscaping. Let’s explore some of the different types of smart irrigation technologies available in the market.
Drip Irrigation, Smart irrigation systems
Drip irrigation is a type of smart irrigation technology that delivers water directly to the roots of plants through a network of tubing, emitters, and valves. This method helps conserve water by minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it one of the most efficient irrigation systems available. Some advantages of using drip irrigation in smart systems include:
- Reduces water waste: Drip irrigation delivers water precisely where it is needed, minimizing water waste and promoting healthier plant growth.
- Improves plant health: By providing a consistent water supply to the roots, drip irrigation helps plants thrive and reduces the risk of diseases caused by overwatering.
- Saves time and labor: Drip irrigation systems are automated and require minimal maintenance, saving time and labor for farmers and gardeners.
Mobile Applications for Remote Monitoring and Control
Integration of mobile applications in smart irrigation systems allows users to monitor and control their irrigation systems remotely, providing real-time data on soil moisture levels, weather conditions, and water usage. Some benefits of using mobile applications for smart irrigation include:
- Enhanced efficiency: Users can adjust irrigation schedules and settings on-the-go, optimizing water usage based on real-time data and weather forecasts.
- Water conservation: Remote monitoring helps prevent water waste by ensuring that irrigation is only applied when necessary, reducing overall water consumption.
- User-friendly interface: Mobile applications provide a user-friendly interface for managing irrigation systems, making it easier for users to track and adjust their watering schedules.
Water Conservation and Efficiency
Smart irrigation systems play a crucial role in water conservation and efficiency by utilizing advanced technologies to optimize water usage in agricultural practices. These systems help reduce water wastage, improve crop yields, and promote sustainable farming practices.
Improving Water Use Efficiency
Smart irrigation systems achieve water conservation and efficiency through various methods, such as:
- Soil moisture sensors: These sensors monitor the moisture levels in the soil and provide data to determine the exact amount of water needed by the plants, preventing over-irrigation.
- Weather-based controllers: These controllers adjust irrigation schedules based on weather conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and rainfall forecasts, to avoid unnecessary watering.
- Drip irrigation systems: Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing evaporation and runoff, thus maximizing water use efficiency.
Reducing Water Wastage in Agriculture
Smart irrigation systems significantly reduce water wastage in agriculture by:
- Preventing over-irrigation: By accurately measuring soil moisture levels and plant water needs, smart systems avoid excessive watering that can lead to water wastage.
- Optimizing irrigation schedules: Smart systems adjust irrigation timing and frequency based on real-time data, ensuring that water is applied only when necessary, reducing unnecessary wastage.
- Promoting precision agriculture: Smart irrigation technologies enable farmers to apply water precisely where and when it is needed, minimizing water losses and maximizing crop production.
Installation and Maintenance
Installing a smart irrigation system involves several key steps to ensure proper functionality and efficiency. Regular maintenance is also crucial for the optimal performance of these systems, helping to prevent issues and maximize water savings. Additionally, understanding how to troubleshoot common problems that may arise is essential for keeping your smart irrigation system running smoothly.
Installation of Smart Irrigation Systems
- Choose the right location for your control panel and sensors to ensure optimal coverage and connectivity.
- Install weather sensors to allow the system to adjust watering schedules based on real-time weather conditions.
- Connect the system to your existing irrigation infrastructure, making sure all components are properly linked and functioning.
- Set up the controller and program watering schedules based on plant types, soil moisture levels, and other specific needs.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
- Regularly check and clean sensors to ensure accurate data collection and watering adjustments.
- Inspect irrigation lines and sprinklers for leaks, clogs, or damage that could affect water distribution.
- Update the system software and firmware as needed to access the latest features and improvements.
- Calibrate the system periodically to account for changes in plant growth, weather patterns, and other factors.
Troubleshooting Smart Irrigation Systems
- Check for connectivity issues between the control panel and sensors, ensuring a stable connection for data transmission.
- Verify that weather sensors are functioning properly and providing accurate information for the system to adjust watering schedules accordingly.
- Inspect the controller settings and programming to identify any errors or conflicts that may be causing irregular watering patterns.
- Consult the user manual or contact technical support for guidance on resolving more complex issues that may arise.
Question & Answer Hub: Smart Irrigation Systems
How do smart irrigation systems differ from traditional methods?
Smart irrigation systems utilize sensors and data to optimize water usage, unlike traditional methods that rely on manual intervention.
What are the benefits of using drip irrigation in smart systems?
Drip irrigation reduces water wastage and ensures targeted delivery to plants, promoting water efficiency and plant health.
How can mobile applications enhance smart irrigation systems?
Mobile apps allow for remote monitoring and control of irrigation systems, enabling farmers to make real-time adjustments for optimal efficiency.